Buzzreach supports the revitalization of specific clinical research and investigator-initiated clinical trials in Japan. Launches project management support service utilizing StudyWorks® and specialized personnel.
Press
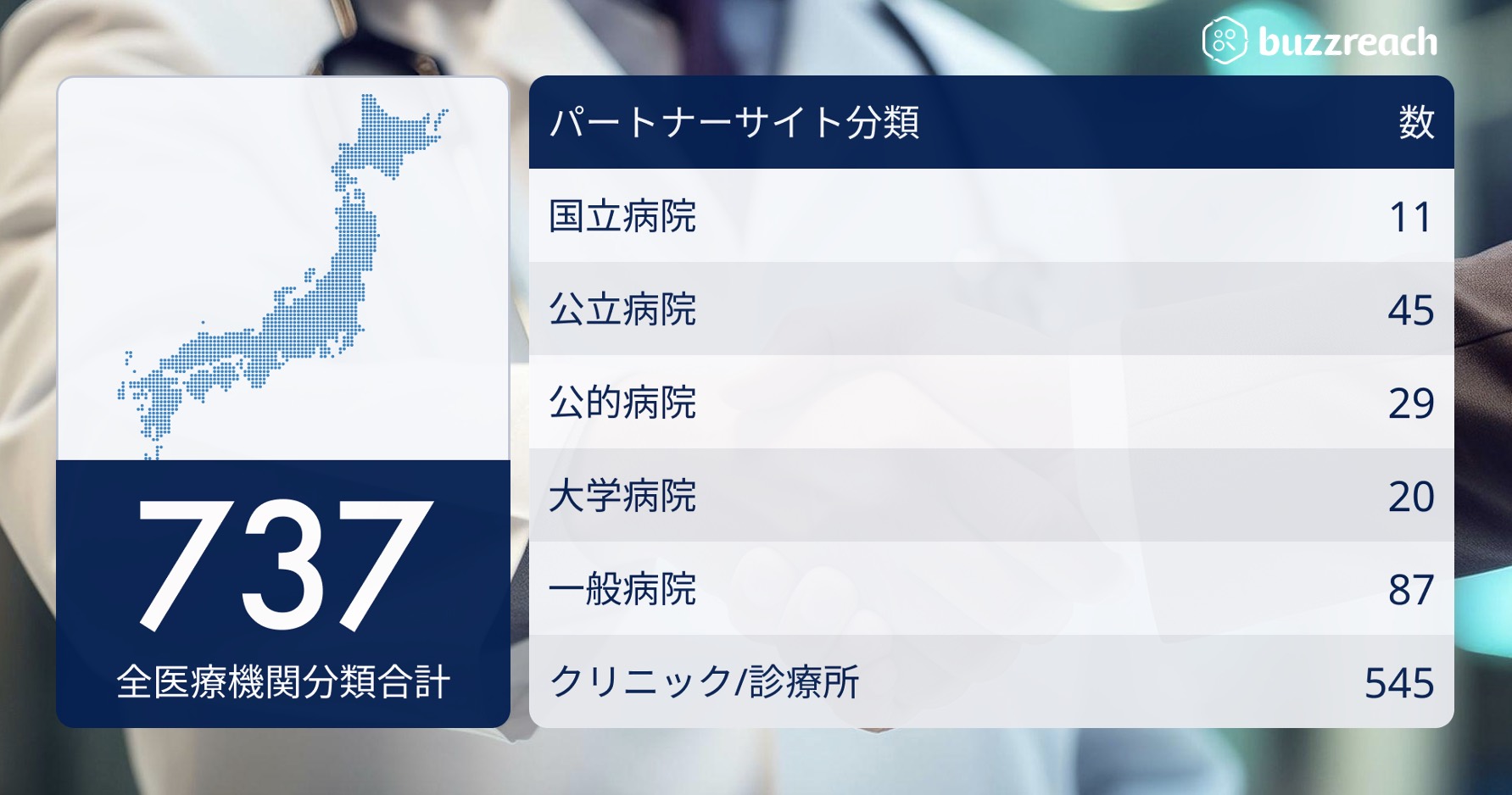
The “Partner Site” network now covers 29 diseases and exceeds 737 facilities

— With a proven track record in 29 diseases, including rare diseases, oncology, and infectious diseases, decentralized management of DCT clinical trial operations will also begin this summer —
Buzzreach Inc. (Headquarters: Minato-ku, Tokyo; Representative Director and CEO: Takateru Inokawa) has signed contracts with 737 facilities across 29 diseases as of May 2025 under its “Partner Site” scheme, which collaborates with medical institutions across the country to introduce patients to participate in clinical trials and support some clinical trial operations on behalf of clinical trial medical institutions .
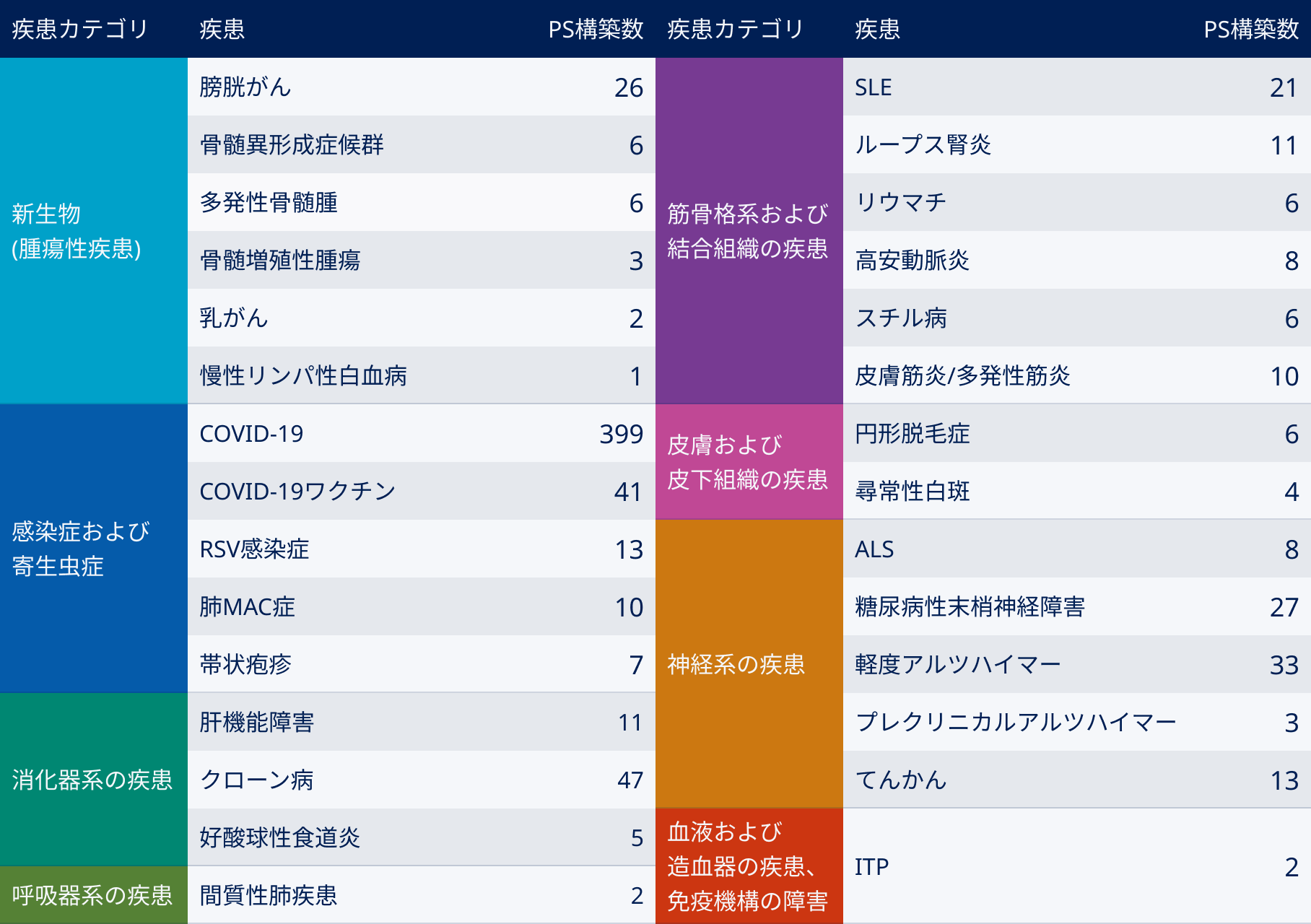
Since its founding, Buzzreach has anticipated the spread of decentralized clinical trials (DCT), and has supported patient recruitment for clinical trials by partnering with medical institutions across Japan (cooperating medical institutions). In particular, the company has a track record of utilizing partner site systems for 29 diseases, including infectious diseases, cancer, and rare diseases, and boasts one of the largest disease coverage ranges and number of contracts in the industry .
■ Partner sites covering 737 facilities and medical institutions nationwide
The partner sites that Buzzreach has worked with to date are built across a wide range of medical institutions and disease types, as shown below, but the purposes for using partner sites can be broadly categorized into two categories.
Case 1: Small number of patients and difficulty in recruiting
Areas where the patient population is small and it is difficult for a single medical institution to accumulate cases, such as intractable and rare diseases such as SLE (including lupus nephritis), ALS, and IBD, mild Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer.
Case 2: Activating entry speed and case accumulation
Areas where a certain number of patients are in the CNS field, such as obesity, dyslipidemia, MASH, and depression, and where case accumulation is carried out with the aim of activating and speeding up entry plans.
■ Partner site operations and Buzzreach’s strengths
Buzzreach does not simply pursue an expansion of the number of sites, but has established a unique “wet” (analog) system in which recruitment managers, comprised of experienced CRCs and CRAs , are responsible for building relationships with and following up on each site. In the “dry” (digital) field, screening for each clinical trial, referral process management, and sharing of patient background information can be centrally managed to reduce the workload of partner sites. This hybrid operation of “wet” and “dry” increases the actual momentum for clinical trials leading to patient referrals.

■ Promotion of DCT and future evolution of partner sites
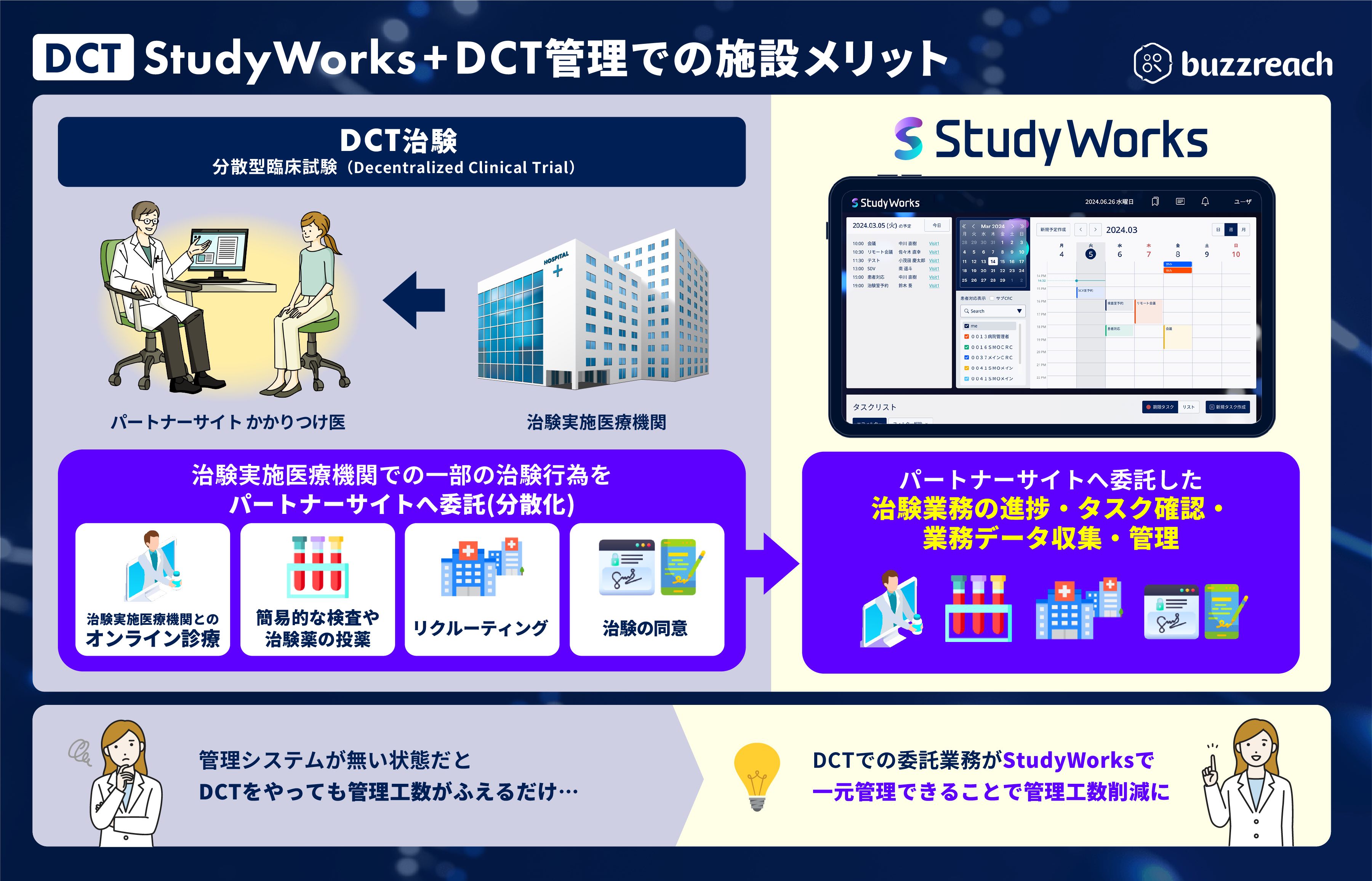
As the government promotes DCT and deregulates GCP*, the range of clinical trial tasks that can be outsourced to partner sites is expanding, from recruiting support (e-recruitment) to clinical trial consent (e-consent) and clinical trial support (visit correspondence, online consultations, home nursing, etc.). Clinical trial sites are now required to understand the content of these outsourced tasks (responsibility for management and supervision within the scope of Article 39-2 of the GCP Ministerial Ordinance). Until now, each DCT task had to be managed separately, which increased the burden on clinical trial sites and raised concerns about an environment that is the exact opposite of promoting DCT. To address these issues, we are adding a function to centralize DCT task management to our clinical trial management platform for clinical trial sites, “StudyWorks,” and will begin partial availability this summer.
*GCP: “Ministerial Ordinance on Standards for the Conduct of Clinical Trials of Pharmaceuticals” (GCP: Good Clinical Practice) established by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare .
In promoting DX in Japan’s clinical trials, Japan has the world’s largest number of medical institutions, and while the role of clinical trial medical institutions is being consolidated at large-scale hospitals such as university hospitals, group hospitals, and cancer centers from the perspective of decentralized clinical trials (DCT), decentralizing some of the various clinical trial tasks, including patient recruitment, will make it possible to revitalize clinical trials throughout Japan. Furthermore, the increased role of partner sites will increase the number of clinical trial treatment options available to doctors and patients not involved in clinical trials, providing a clue to resolving the information gap and insufficient patient recruitment issues that are one of the challenges facing the Japanese clinical trial environment, and ultimately contributing to the elimination of drug lag/loss.








